澤龜日常攝取富含幾丁質的節肢動物,能提供高品質蛋白質與營養,且可被其消化系統順利分解,不影響脂溶性維生素吸收。研究顯示,幾丁質對澤龜的健康有多項益處!
【鮮蝦研究室】澤龜的營養需求與對幾丁質的攝取(下)

台大水生動物博士/鮮蝦食譜研發𝗥&𝗗
◑攝入幾丁質是澤龜飲食的日常

節肢動物是提供澤龜高品質蛋白質、必需胺基酸與其他營養物質的重要來源。因此,節肢動物及其成份也是人為飼養澤龜時常採用的餌食主要成份之一。包括鮮蝦食譜在內,目前市面上可取得的各品牌澤龜飼料中,有超過八成的產品在原料中都有使用節肢動物或其成份 (圖1);而以節肢動物為最主要成份 (即原料標示中排名第一位者) 的飼料產品就佔了市面上可取得的3成以上 (圖2)。
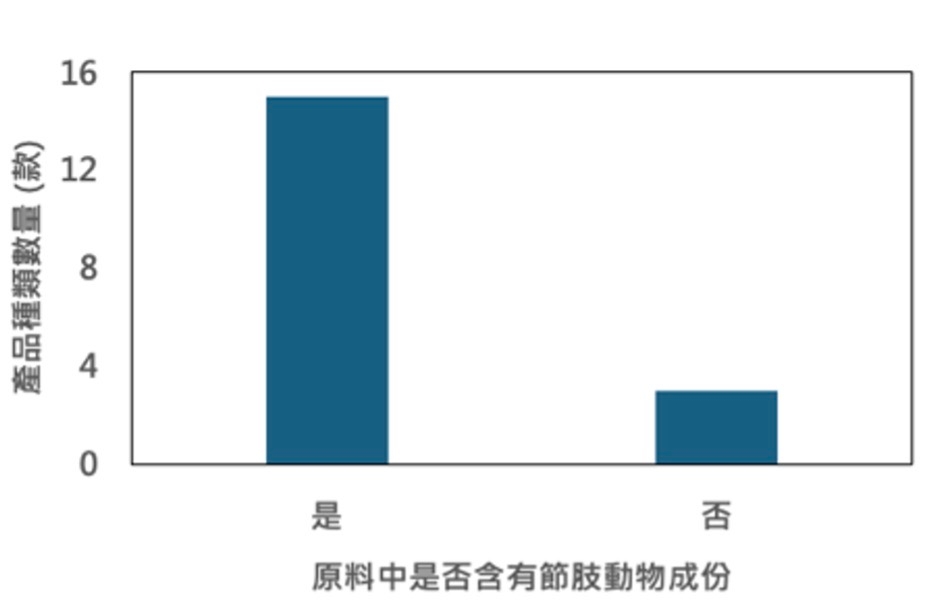 圖1. 市售澤龜飼料原料中有使用節肢動物或其成分的種數
圖1. 市售澤龜飼料原料中有使用節肢動物或其成分的種數
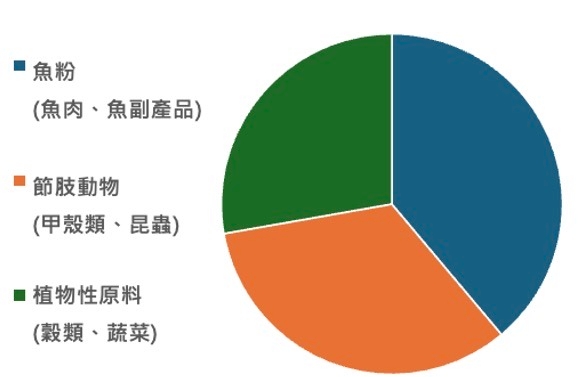 圖2. 市售澤龜飼料使用的主要原料
圖2. 市售澤龜飼料使用的主要原料
節肢動物的主要特徵之一,就是牠們身體的表面都具有以幾丁質 (chitin) 為主要成份的外骨骼,包含蝦、螯蝦、昆蟲等在內。幾丁質是一種含氮多醣類的聚合物,由一個一個稱為「N-乙醯葡萄糖胺 (N-acetylglucosamine)」的單體以(1 -> 4) 醣苷鍵 (β-(1->4)-glycosidic bond) 串接起來,如同鎖鏈般形成長鏈狀,結構上跟纖維素 (cellulose) 相似,也都有類似的堅韌特性。這樣一來,不免讓人懷疑,幾丁質的質地堅韌有彈性,若澤龜吃多了這些富含幾丁質的無脊椎動物之後,腸胃是不是會被幾丁質阻塞、或是阻礙營養成份的吸收?關於這點應該可以不用擔心,因為幾丁質在澤龜消化道裡是能夠被充份分解的。
本系列先前的專文【劍蝦飼料中的甲殼素是否影響觀賞魚的營養吸收?】曾經談論過,在自然界中就存在有可以分解幾丁質的酵素,它們可以把長鏈狀結構的幾丁質打斷,再透過其他酵素的一連串作用最終將幾丁質分解成醣類,作為營養能量的來源之一。主要打斷 (分解) 幾丁質結構的酵素稱為幾丁質酶 (chitinase),並且可以再根據其作用在幾丁質結構上不同的位置被細分為數種酶。在會進食昆蟲等無脊椎動物的爬蟲類體內,包括澤龜的腸胃道和胰臟裡,已經被證實會分泌具有分解幾丁質的酵素。
◑餵食含幾丁質飼料與維生素A缺乏沒有關係

關於澤龜對幾丁質的攝取坊間還有流傳一個傳言,認為「甲殼素」會在澤龜的腸胃道表面阻礙脂質和營養的吸收,使得澤龜對脂溶性營養成份 (例如脂溶性維生素) 的吸收不足,所以食物或飼料中如果含有大量甲殼素的話,澤龜會營養不良,最常被提及就是維生素A缺乏造成的澤龜眼睛腫漲症狀。
在前述的專文中也說明過,幾丁質被俗稱為甲殼素,但另外一個多醣聚合物-幾丁聚醣 (也稱為殼聚醣;chitosan) 也被俗稱為甲殼素。雖然幾丁聚醣是以幾丁質為原料透過生物工程的方式所反應產生出來的,但兩者在結構上和性質上並不相同。根據動物實驗觀察的結果,會在腸道表面形成膠狀屏障並留滯脂質與膽固醇、降低它們的吸收,降低血中膽固醇濃度的是幾丁聚醣,並非幾丁質。而且,坊間以保健食品名義、主訴可以阻斷脂肪吸收進行販售的甲殼素產品,有效的成份也不是作為原料的幾丁質,而是反應之後佔比至少需達70%-90%的產物--幾丁聚醣。到目前為止,科學上並未證實幾丁質會在澤龜的消化道中轉變成幾丁聚醣並且形成膠狀屏障而阻礙營養成份的吸收。反而,在澤龜的菜單加上甲殼類、昆蟲等富含幾丁質的成份,其實是更符合牠們在野外的食物組成狀況 (表1)。
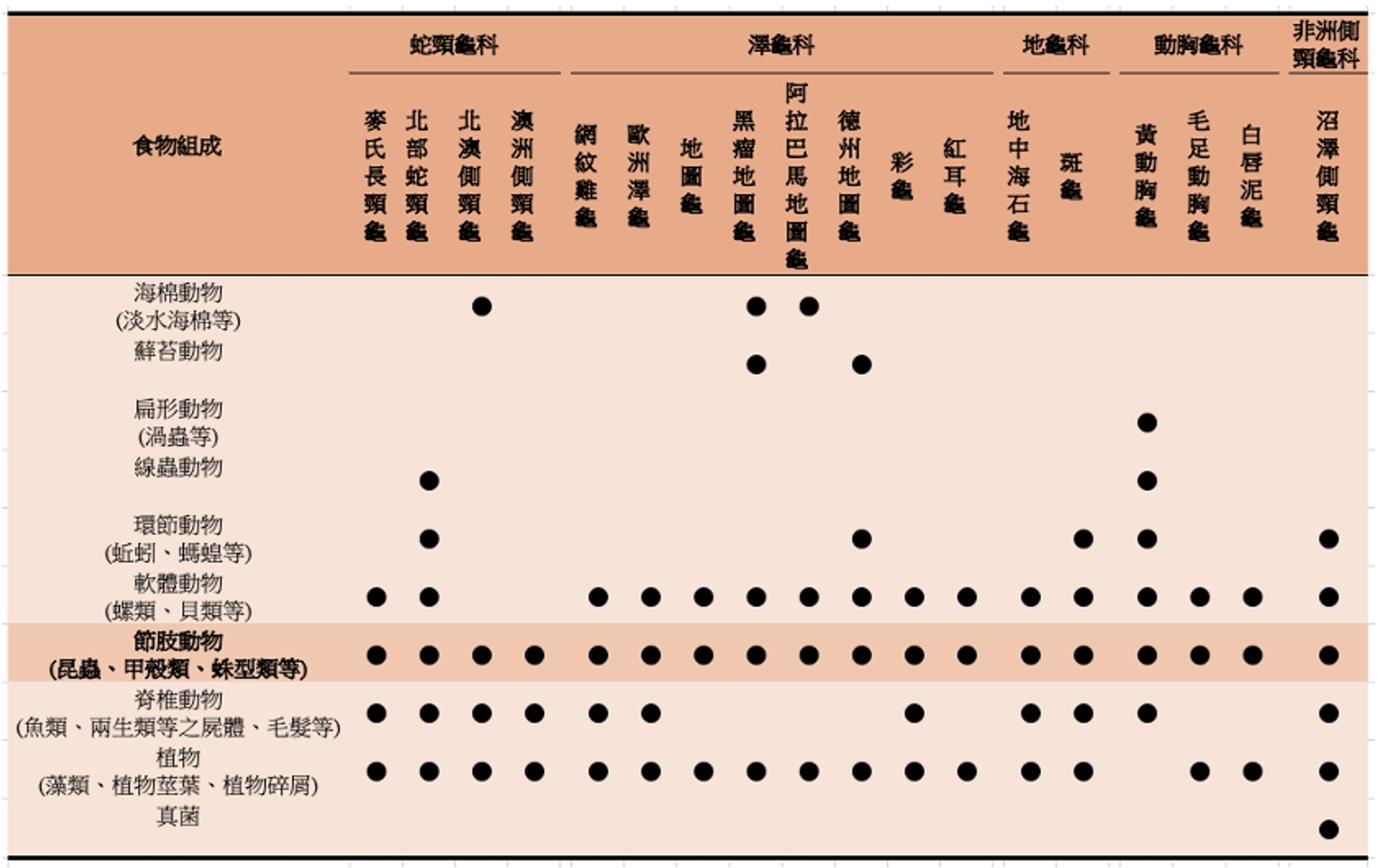 表1.部分種類澤龜於野外的食物組成
表1.部分種類澤龜於野外的食物組成
在人為飼養環境下澤龜出現拒食、動作遲緩、眼睛(眼皮)腫脹甚至近瞎的情況,至少早在60年前就已經被歐洲的爬蟲獸醫與學者提及並研究。最常出現拒食、活力降低、眼睛緊閉、腫脹甚至近瞎的個體,尤其以剛孵化後沒多久就被大量輸入到寵物市場中的幼龜為多。這些病龜除了眼睛(眼皮)的腫脹之外,在肝臟、胰臟與腎臟的腺體分泌小管上也會出現大規模的上皮化生現象 (epithelial metaplasia;也就是該處的上皮細胞被另外一種細胞所替代的過程),而這與出現在人類和其他動物的維生素A缺乏症 (avitaminosis A) 所造成的症狀相仿。因此,當澤龜出現這些症狀時,很合理地被懷疑是跟牠體內缺乏維生素A有關。目前,一般針對這類症狀的治療也常以補充大量維生素A的方式進行。不過,關於澤龜出現異常狀況時的處理與治療細節需交由專業的爬蟲專科獸醫師來判斷診療與執行指導,在此就不贅述。澤龜體內維生素A不足的原因,目前普遍被認為與透過食物的攝取不足所導致。因此,長時間的飢餓與餵食量不足、餌食種類過於單一 (特別是單一生餌的使用)、餵食的生餌中維生素A含量過低、選擇的飼料製程過程不恰當而破壞維生素A等都是可能的原因,但到目前為止並沒有任何證據顯示是跟飼料中是否含有幾丁質成份有關。
為了預防澤龜包含維生素A在內可能的維生素缺乏疑慮,現在的澤龜飼料生產商其實也作了應對,在飼料配方設計上透過額外增加含脂溶性維生素或其前驅物的成份來適量提高脂溶性維生素的可獲得性。因此,如果仔細看,目前所有合法廠商上市的澤龜飼料原料表中都會標註維生素的額外添加。另外,如果是澤龜的飼養者,則可以透過選擇合法廠商生產、原料多元且配方設計適當的澤龜飼料來降低營養素失衡的狀況。甚至,澤龜飼主在有餘力之時,還可以偶爾額外準備適合的生鮮食材生餌,清洗乾淨後搭配飼料一起進行餵食。
◑澤龜攝取富含幾丁質的食物:目前的科學證據顯示多有益處!

事實上,幾丁質和其衍生物 (包含幾丁聚醣) 在加速傷口癒合、具有抗菌活性、可增強免疫活性等多個方面都有相關研究被報導。只是,澤龜在攝取幾丁質 (或其衍生物) 或富含幾丁質的食物後,其營養和健康狀況與未攝取者是否有任何的差別,相關的研究與報導仍待累積中。近年,有研究報導,以黑水虻幼蟲粉適量取代魚粉製成飼料餵飼豢養於實驗室的紅腹側頸龜 (Emydura subglobosa) 和中華龞 (Pelodiscus sinensis) 長達70天後,不僅可以讓牠們正常生長,更在抗氧化能力、腸道消化酵素活性、肌肉生化指數等都有正面的效果。
◑鮮蝦食譜澤龜飼料全系列含天然劍蝦、綜合維生素、脂溶性維生素前驅物

坊間有許多澤龜飼料商品會特別額外添加昆蟲粉、磷蝦粉、甲殼素,以增加飼料中的甲殼素含量供澤龜攝取。鮮蝦食譜澤龜飼料全系列,包含【挑嘴幼澤龜】、【挑嘴亞成澤龜】 與【挑嘴 巴西龜&各種成澤龜】,以天然劍蝦、日本毛蝦全蝦等為原料,直接提供澤龜優質且足量的蛋白質與胺基酸以及天然的幾丁質。此外,鮮蝦食譜澤龜飼料採用的植物性原料含有豐富的維生素、維生素前驅物、礦物質與微量元素。使用穩定型態的維生素補足飼料製程裡原料中部份流失的維生素;全蝦、桑葉與沙丁魚全魚提供澤龜成長與日常生理作用所需的鈣質與礦物質;專利除臭益生菌可以強效分解排泄物中的惡臭物質,降低水質臭味和污濁。鮮蝦食譜澤龜飼料全系列的配方設計同時兼顧澤龜在不同生長階段所需的所有營養需求,嗜口性優於坊間同類型商品,也降低飼主在飼養過程中對水質與排泄物的不佳感受,大大降低了澤龜飼養的難度。

◑參考文獻
Ceballos C. P., Zapata D., Alvarado C., Rincon E. (2016) Morphology, diet, and population structure of the southern white-lipped mud turtle Kinosternon leucostomum postinguinale (Testudines: Kinosternidae) in the Nus River drainage, Colombia. Journal of Herpetology 50(3): 374-380.
Chen T.-H., Lue K.-Y. (1998) Ecology of the Chinese stripe-necked turtle, Ocadia sinensis (Testudines: Emydidae), in the Keelung River, northern Taiwan. Copeia 1998(4): 944-952.
Chen T.-H., Lue K.-Y. (1999) Food habits of the Chinese stripe-necked turtle, Ocadia sinensis, in the Keelung River, northern Taiwan. Journal of Herpetology 33(3): 463-471.
Cloudsley-Thompson J. L. (1999) Nutritional Diversity. In: The Diversity of Amphibians and Reptiles: An Introduction, pp 109-129.
Da Costa Araujo J., e Rosa P.V., das Dores Correia Palha M., Rodrigues P.B., de Freitas R.T.F., do Socorro Lima da Silva A. (2013) Effect of three feeding management systems on some reproductive parameters of Scorpion mud turtles (Kinosternon scorpioides) in Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 45: 729-735.
Demuth J. P., Buhlmann K. A. (1997) Diet of the turtle Deirochelys reticularia on the Savannah River site, South Carolina. Journal of Herpetology 31(3): 450-453.
Gades M.D., Stern J.S. (2003) Chitosan supplementation and fecal fat excretion in men. Obesity Research 11(5): 683-688.
Gibbons J.W. ed. (1990) Life history and ecology of the slider turtle. Waschington D.C., USA, Smithsonian Institution Press.
Jeuniaux C. (1961) Chitinase: an addition to the list of hydrolases in the digestive tract of vertebrates. Nature 192(4798): 135-136.
Kennett Rod., Tory O. (1996) Diet of two freshwater turtles, Chelodina rugosa and Elseya dentata (Testudines: Chelidae) from the wet-dry tropics of northern Australia. Copeia 1996(2): 409-419.
Koide S.S. (1998) Chitin-chitosan: properties, benefits and risks. Nutrition. research 18(6): 1091-1101.
Kou S., Peters L., Mucalo M. (2021) Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 169: 85-94.
Kumar M.N.V.R. (2000) A review of chitin and chitosan applications. Reactive and functional polymers 46(1): 1-27.
Lindeman P. V. (2006) Diet of the Texas map turtle (Graptemys versa): relationship to sexually dimorphic trophic morphology and changes over five decades as influenced by an invasive mollusk. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 5(1): 25-31.
Lindeman P. V. (2016) Diets of syntopic black-knobbed sawbacks (Graptemys nigrinoda) and Alabama map turtles (Graptemys pulchra) in the Alabama River. The American Midland Naturalist 175: 194-205.
Luiselli L., Akani G.C., Ebere N., Rugiero L., Vignoli L., Angelici F.M., Eniang E.A., Behangana M. (2011) Food Habits of a Pelomedusid Turtle, Pelomedusa subrufa, in Tropical Africa (Nigeria): The Effects of Sex, Body Size, Season, and Site. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 10(1):138- 144.
McArthur S., Wilkinson R., Meyer J, ed. (2008) Medicine and surgery of tortoises and turtles. John Wiley & Sons.
Ottonello D., Salvidio S., Rosecchi E. (2005). Feeding habits of the European pond terrapin Emys orbicularis in Camargue (Rhône delta, Southern France). Amphibia-Reptilia 26:562-565.
Pérez-Santigosa N., Florencio M., Hidalgo-Vila J., Diaz-Paniagua C. (2011) Does the exotic invader turtle, Trachemys scripta elegans, compete for food with coexisting native turtles?. Amphibia-Reptilia 32(2): 167-175.
Platt S.G., Berezin A.R., Miller D.J., Rainwater T.R. (2016) A dietary study of the rough-footed mud turtle (Kinosternon hirtipes) in Texas, USA. Herpetological Conservation and Biology 11(1): 142-149.
Punzo F. (1974) A qualitative and quantitative study of the food items of the yellow mud turtle, Kinosternon flavescens (Agassiz). Journal of Herpetology 8(3): 269-271.
Rawski M., Mans C., Kieronczyk B., Swiakiewicz S., Barc A., Jozefiak D. (2018) Freshwater turtle nutrition–a review of scientific and practical knowledge. Annals of Animal Science 18(1): 17-37. DOI: 10.1515/aoas-2017-0025.
Rawski M., Kieronczyk B., Hetmanczyk H., Jozefiak D., Skrzypczak P., Mazurkiewicz J. (2024) The first report of the growth performance and environmental sustainability effects of dietary insect meal application on the Jardine River turtle (Emydura subglobosa). Annals of Animal Science, DOI: 10.2478/aoas-2024-0037.
Rhodin A.G.J., Ibarrondo B.R., Kuchling G. (2008). Chelodina mccordi Rhodin 1994—Roti Island snake-necked turtle, McCord’s snake-necked turtle, kura-kura rote. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 5: 001-008.
Richards-Dimitrie T., Gresens S.E., Smith S.A., Seigel R.A. (2013) Diet of Northern Map Turtles (Graptemys geographica): sexual differences and potential impacts of an altered river system. Copeia 2013(3): 477-484.
Shang R., Man L., Wang G., Li M., Liu C., Li L. (2022) Influences of partial substitution of fish meal with defatted black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets on growth performance, biochemical parameters, and body composition of juvenile Chinese soft-shelled turtles (Pelodiscus sinensis). Aquaculture Nutrition 2022: 1-10.
Spencer R.-J., Thompson M.B., Hume I.D. (1998). The diet and digestive energetics of an Australian short-necked turtle, Emydura macquarii. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A. 121: 341- 349.
Tsigos I., Martinou A., Kafetzopoulos D., Bouriotis V. (2000) Chitin deacetylases: new, versatile tools in biotechnology. Trends in biotechnology 18(7): 305-312.
Works A. J., Olson D.H. (2018) Diets of two nonnative freshwater turtle species (Trachemys scripta and Pelodiscus sinensis) in Kawai Nui Marsh, Hawaii. Journal of Herpetology 52(4): 444-452.
#澤龜 #澤龜營養 #烏龜 #烏龜飼料 #澤龜飼料 #澤龜飼養 #澤龜飼料推薦


 繁體中文
繁體中文 English
English